How To Install Ati Video Driver In Ubuntu
Posted By admin On 16.08.19Contents
|
This guide shows you how to use the open source Radeon driver for some ATI/AMD graphics cards and APUs, which is part of the xserver-xorg-video-ati package.
This driver provides 2D and 3D acceleration in your video hardware. For the most recent releases of Ubuntu (and its flavours) this driver is usually as fast as the closed-source, proprietary fglrx driver (called AMD Catalyst) from AMD Inc. Furthermore the Radeon driver supports some older chipsets that fglrx does not.
The Radeon driver is already pre-installed in Ubuntu.
First, check your graphic card name and chipset:
It should report something like this for your graphics card and/or APU:
If the report shows two different hardware devices, then you probably have a 'hybrid graphics' system, with an iGP (integrated graphics processor inside the CPU) and a dedicated GPU.
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and newer: for some most recent graphics cards (R9 285, R9 380/380X, R9 M395X, R9 Nano/Fury/FuryX, RX 460/470/480, RX 550/560/570/580...) and APUs (Carrizo, Stoney), the open-source AMDGPU driver is enabled by default. For Ubuntu 16.04 LTS AMDGPU-Pro hybrid driver is also available to download here (please read the release notes for known problems and limitations).
Ubuntu 14.04 LTS: if you have Ubuntu 14.04 LTS with Linux kernel 4.4.0 (HWE stack Xenial), you can't install the proprietary fglrx/Catalyst driver. However the open source AMDGPU driver is available to install through the xserver-xorg-video-amdgpu package.
These cards will not run Ubuntu's Unity desktop with 3D acceleration. They will still run Unity, but the CPU will be used for basic drawing and performance may suffer. If you have one of these cards, a lighter desktop (such as XFCE or LXDE, found in Xubuntu and Lubuntu respectively) is recommended.
Chipset | Graphics cards |
R100 | Radeon 7200 |
RV100 | Radeon 7000(VE), M6, RN50/ES1000 |
RS100 | Radeon IGP320(M) |
RV200 | Radeon 7500, M7, FireGL 7800 |
RS200 | Radeon IGP330(M)/IGP340(M) |
RS250 | Radeon Mobility 7000 IGP |
R200 | Radeon 8500, 9100, FireGL 8800/8700 |
RV250 | Radeon 9000PRO/9000, M9 |
RV280 | Radeon 9200PRO/9200/9200SE/9250, M9+ |
RS300 | Radeon 9100 IGP |
RS350 | Radeon 9200 IGP |
Whoever is maintaining this article should make an update. I recently used Kubuntu with an ATI Radeon graphics card and not only I have the default Radeon drivers in. Download AMD Drivers & Software for Radeon, FirePro, APU, CPU, desktops, and laptops.
All these ATI/AMD cards have good 3D acceleration support. This is not an exhaustive list.
Check the version of Ubuntu you have installed:
Ubuntu 16.04 and newer releases: look at the 16.04+ column.
Ubuntu 14.04:
kernel Linux 4.4.0-xx-generic (HWE stack Xenial), look at the 16.04+ column.
kernel Linux 3.13.0-xx-generic, look at the 14.04 column.
Ubuntu 12.04:
kernel Linux 3.13.0-xx-generic (HWE stack Trusty), look at the 14.04 column.
kernel Linux 3.2.0-xx-generic, look at the 12.04 column.
To know which version of the Linux kernel you have installed, type this text in a terminal window: uname -r |
In Ubuntu 12.04 LTS with the 3.2.0-xx-generic Linux kernel, you might encounter overheating problems of the graphics card, which are caused by the too old Radeon driver installed in Ubuntu. In this case, you can install the Trusty Hardware Enablement Stack, which brings new versions of Linux kernel and Radeon driver. This generally solves the problem. |
Chipset | Graphics cards and APUs | 12.04 | 14.04 | 16.04+ |
RS400/RS480 | Radeon XPRESS 200(M)/1100 IGP | |||
R300 | Radeon 9700PRO/9700/9500PRO/9500/9600TX, FireGL X1/Z1 | |||
R350 | Radeon 9800PRO/9800SE/9800, FireGL X2 | |||
R360 | Radeon 9800XT | |||
RV350 | Radeon 9600PRO/9600SE/9600/9550, M10/M11, FireGL T2 | |||
RV360 | Radeon 9600XT | |||
RV370 | Radeon X300, M22 | |||
RV380 | Radeon X600, M24 | |||
RV410 | Radeon X700, M26 PCIE | |||
R420 | Radeon X800 AGP | |||
R423/R430 | Radeon X800, M28 PCIE | |||
R480/R481 | Radeon X850 PCIE/AGP | |||
RV505/RV515/RV516/RV550 | Radeon X1300/X1400/X1500/X1550/X2300 | |||
R520 | Radeon X1800 | |||
RV530/RV560 | Radeon X1600/X1650/X1700 | |||
RV570/R580 | Radeon X1900/X1950 | |||
RS600/RS690/RS740 | Radeon X1200/X1250/X2100 | |||
R600 | Radeon HD 2900 | |||
RV610/RV630 | Radeon HD 2400/2600/2700/4200/4225/4250 | |||
RV620/RV635 | Radeon HD 3410/3430/3450/3470/3650/3670 | |||
RV670 | Radeon HD 3690/3850/3870 | |||
RS780/RS880 | Radeon HD 3100/3200/3300/4100/4200/4250/4290 | |||
RV710/RV730 | Radeon HD 4330/4350/4550/4650/4670/5145/5165/530v/545v/560v/565v | |||
RV740/RV770/RV790 | Radeon HD 4770/4730/4830/4850/4860/4870/4890 | |||
CEDAR | Radeon HD 5430/5450/6330/6350/6370 | |||
REDWOOD | Radeon HD 5550/5570/5650/5670/5730/5750/5770/6530/6550/6570 | |||
JUNIPER | Radeon HD 5750/5770/5830/5850/5870/6750/6770/6830/6850/6870 | |||
CYPRESS | Radeon HD 5830/5850/5870 | |||
HEMLOCK | Radeon HD 5970 | |||
PALM | Radeon HD 6310/6250 | |||
SUMO/SUMO2 | Radeon HD 6370/6380/6410/6480/6520/6530/6550/6620 | |||
BARTS | Radeon HD 6790/6850/6870/6950/6970/6990 | |||
TURKS | Radeon HD 6570/6630/6650/6670/6730/6750/6770 | |||
CAICOS | Radeon HD 6430/6450/6470/6490 | |||
CAYMAN | Radeon HD 6950/6970/6990 | |||
ARUBA | Radeon HD 7000 series | |||
TAHITI | Radeon HD 7900 series | |||
PITCAIRN | Radeon HD 7800 series | |||
VERDE | Radeon HD 7700 series | |||
OLAND | Radeon HD 8000 series | |||
HAINAN | Radeon HD 8800 series | |||
BONAIRE | Radeon HD 7790 series | |||
KAVERI | KAVERI APUs | |||
KABINI | KABINI APUs | |||
HAWAII | Radeon R9 290/290X/390/390X | |||
MULLINS (Puma/Puma+ cores, GCN GPU) | MULLINS/BEEMA/CARRIZO-L APUs |
Notes
*1: in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS with Linux kernel 3.13.0 if you find problems with the most recent graphics cards (Radeon Rx 2xx/3xx) and APUs (KABINI/KAVERI), try to install the Xenial HWE stack in Ubuntu 14.04; this should solve your problems. As an alternative, you can install a newer release of Ubuntu.
To look for boot messages/errors, check
To see your OpenGL information, you can run the commands below. Make sure your OpenGL renderer string does not say 'software rasterizer' or 'llvmpipe' because that would mean you have no 3D hardware acceleration:
If you've previously installed the ATI binary/proprietary driver (a.k.a Catalyst/fglrx), you need to make sure it's fully purged before trying to use the open-source ati/radeon driver. See this page
No configuration is necessary for ATI driver in the modern versions of Ubuntu. You can safely take away your /etc/X11/xorg.conf and your computer should run fine.
Check the manpage of the Radeon driver for advanced options.
Ubuntu 14.04 and newer: HDMI audio should work automatically.
Ubuntu 12.04: users have to enable HDMI audio manually by passing the radeon.audio=1 kernel parameter. It can be done with the following command:
Ubuntu Precise/12.04 users should also note that they may need a newer kernel (>= 3.5.x) to enable HDMI audio on later cards.
Ubuntu 12.04.5 LTS (Linux kernel 3.13.0), Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and later
For the most recent ATI/AMD graphic cards supported by the Radeon driver, DPM (Dynamic Power Management) should work automatically without additional steps.
Instead if you notice overheating problems and/or you have an old Radeon HD graphic card, you can enable DPM by adding a boot parameter. This should greatly help power consumption, especially when idle. To do so, edit /etc/default/grub and add the 'radeon.dpm=1' to the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT line, so it would look something like:
After you save/quit the text editor, update grub:
Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (Linux kernel 3.2.0)
Power management was one of the weak spots of the open-source driver prior to kernel 3.11.x. If you have a laptop that's getting too hot, try setting the power management profile to low.
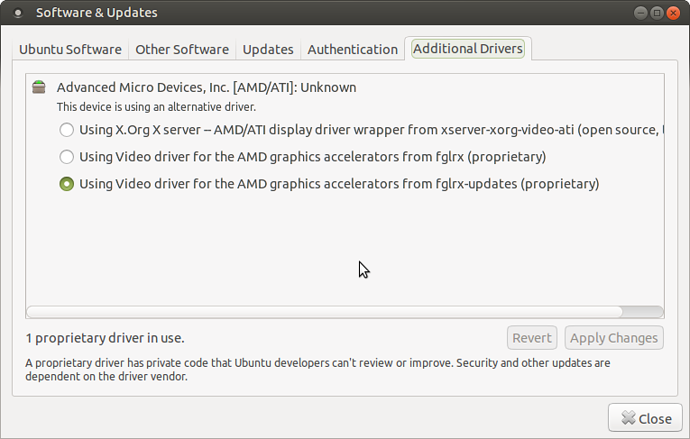
How To Install Ati Fglrx Driver In Ubuntu
BinaryDriverHowto/AMD - The Wiki page for the proprietary AMD/ATI driver 'fglrx' which also offers 3D acceleration, and works on newer cards than the 'radeon' driver. Since it's closed-source, only AMD can work on it and give efficient support, and the open-source community can generally not help you with problems.
AMDGPU-Driver - The Wiki page for AMD's AMDGPU open source driver for GCN (Graphics Core Next) GPUs
AMDGPU-PRO-Driver - The Wiki page for AMD's AMDGPU-PRO hybrid proprietary/open-source driver for GCN (Graphics Core Next) GPUs
Arch Linux ati driver documentation - includes TV-out information
RadeonFeature - Radeon feature table
CategoryHardware
This article covers the radeon open source driver which supports the majority of AMD (previously ATI) GPUs.
- 3Loading
- 5Performance tuning
- 5.4Kernel parameters
- 7Powersaving
- 7.1Dynamic power management
- 7.2Old methods
- 9TV out
- 11Multihead setup
- 13Troubleshooting
Selecting the right driver
Depending on the card you have, find the right driver in Xorg#AMD. This page has instructions for ATI.
If unsure, try this open source driver first, it will suit most needs and is generally less problematic. See the feature matrix to know what is supported and the decoder ring to translate marketing names (e.g. Radeon HD4330) to chip names (e.g. R700).
Installation
Install the mesa package, which provides the DRI driver for 3D acceleration.
- For 32-bit application support, also install the lib32-mesa package from the multilib repostory.
- For the DDX driver (which provides 2D acceleration in Xorg), install the xf86-video-ati package.
Support for accelerated video decoding is provided by mesa-vdpau and lib32-mesa-vdpau packages.
Loading
The radeon kernel module should load fine automatically on system boot.
If it does not happen, then:
- Make sure you do not have
nomodesetorvga=as a kernel parameter, since radeon requires KMS. - Also, check that you have not disabled radeon by using any kernel module blacklisting.
Enable early KMS
See Kernel mode setting#Early KMS start.
Xorg configuration
Xorg will automatically load the driver and it will use your monitor's EDID to set the native resolution. Configuration is only required for tuning the driver.
If you want manual configuration, create /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-radeon.conf, and add the following:
Using this section, you can enable features and tweak the driver settings.
Performance tuning
Enabling video acceleration
See Hardware video acceleration.
Graphical tools
- WattmanGTK — A GTK3 user-interface written in Python 3, which allows you to view, monitor Radeon performance, fan speeds and power states and the ability to overclock the graphics processor. It uses the AMDGPU kernel driver.
amdgpu.ppfeaturemask) in order to enable the AMD Overdrive technology within GNU/Linux. Which is necessary to use WattmanGTK.- radeon-profile — Qt application for displaying info about a Radeon card.
- https://github.com/marazmista/radeon-profile radeon-profile-gitAUR
Driver options
How To Install Ati Drivers In Ubuntu 14.04
The following options apply to /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-radeon.conf.
Please read radeon(4) and RadeonFeature first before applying driver options.
Acceleration architecture; Glamor is available as a 2D acceleration method implemented through OpenGL, and it is the default for R600 (Radeon HD2000 series) and newer graphic cards. Older cards use EXA.
DRI3 is enabled by default since xf86-video-ati 7.8.0. For older drivers, which use DRI2 by default, switch to DRI3 with the following option:
TearFree is a tearing prevention option which prevents tearing by using the hardware page flipping mechanism:
ColorTiling and ColorTiling2D are supposed to be enabled by default. Tiled mode can provide significant performance benefits with 3D applications. It is disabled if the DRM module is too old or if the current display configuration does not support it. KMS ColorTiling2D is only supported on R600 (Radeon HD2000 series) and newer chips:
When using Glamor as acceleration architecture, it is possible to enable the ShadowPrimary option, which enables a so-called 'shadow primary' buffer for fast CPU access to pixel data, and separate scanout buffers for each display controller (CRTC). This may improve performance for some 2D workloads, potentially at the expense of other (e.g. 3D, video) workloads. Note that enabling this option currently disables Option 'EnablePageFlip':
EXAVSync is only available when using EXA and can be enabled to avoid tearing by stalling the engine until the display controller has passed the destination region. It reduces tearing at the cost of performance and has been known to cause instability on some chips:
Below is a sample configuration file of /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-radeon.conf:
Kernel parameters
systool as stated in Kernel modules#Obtaining information.Defining the gartsize, if not autodetected, can be done by adding radeon.gartsize=32 as a kernel parameter.
The changes take effect at the next reboot.
Deactivating PCIe 2.0
Since kernel 3.6, PCI Express 2.0 in radeon is turned on by default.
It may be unstable with some motherboards. It can be deactivated by adding radeon.pcie_gen2=0 as a kernel parameter.
See Phoronix article for more information.
Gallium Heads-Up Display
The radeon driver supports the activation of a heads-up display (HUD) which can draw transparent graphs and text on top of applications that are rendering, such as games. These can show values such as the current frame rate or the CPU load for each CPU core or an average of all of them. The HUD is controlled by the GALLIUM_HUD environment variable, and can be passed the following list of parameters among others:
- 'fps' - displays current frames per second
- 'cpu' - displays the average CPU load
- 'cpu0' - displays the CPU load for the first CPU core
- 'cpu0+cpu1' - displays the CPU load for the first two CPU cores
- 'draw-calls' - displays how many times each material in an object is drawn to the screen
- 'requested-VRAM' - displays how much VRAM is being used on the GPU
- 'pixels-rendered' - displays how many pixels are being displayed
To see a full list of parameters, as well as some notes on operating GALLIUM_HUD, you can also pass the 'help' parameter to a simple application such as glxgears and see the corresponding terminal output:
More information can be found from this mailing list post or this blog post.
Hybrid graphics/AMD Dynamic Switchable Graphics
It is the technology used on recent laptops equiped with two GPUs, one power-efficent (generally Intel integrated card) and one more powerful and more power-hungry (generally Radeon or Nvidia). There are two ways to get it work:
- If it is not required to run 'GPU-hungry' applications, it is possible to disable the discrete card (see Ubuntu wiki):
echo OFF > /sys/kernel/debug/vgaswitcheroo/switch. - PRIME: Is a proper way to use hybrid graphics on Linux, but still requires a bit of manual intervention from the user.
Powersaving
With the radeon driver, power saving is disabled by default and has to be enabled manually if desired.
You can choose between three different methods:
- dpm (enabled by default since kernel 3.13)
See https://www.x.org/wiki/RadeonFeature/#index3h2 for more details.
Dynamic power management
Since kernel 3.13, DPM is enabled by default for lots of AMD Radeon hardware. If you want to disable it, add the parameter radeon.dpm=0 to the kernel parameters.
radeon.dpm=1 kernel parameter will enable dpm.Unlike dynpm, the 'dpm' method uses hardware on the GPU to dynamically change the clocks and voltage based on GPU load. It also enables clock and power gating.
There are 3 operation modes to choose from:
batterylowest power consumptionbalancedsane defaultperformancehighest performance
They can be changed via sysfs
For testing or debugging purposes, you can force the card to run in a set performance mode:
autodefault; uses all levels in the power statelowenforces the lowest performance levelhighenforces the highest performance level
Commandline Tools
- radcard - A script to get and set DPM power states and levels
Old methods
Dynamic frequency switching
This method dynamically changes the frequency depending on GPU load, so performance is ramped up when running GPU intensive apps, and ramped down when the GPU is idle. The re-clocking is attempted during vertical blanking periods, but due to the timing of the re-clocking functions, does not always complete in the blanking period, which can lead to flicker in the display. Due to this, dynpm only works when a single head is active.
It can be activated by simply running the following command:
Profile-based frequency switching
This method will allow you to select one of the five profiles (described below). Different profiles, for the most part, end up changing the frequency/voltage of the GPU. This method is not as aggressive, but is more stable and flicker free and works with multiple heads active.
To activate the method, run the following command:
Select one of the available profiles:
defaultuses the default clocks and does not change the power state. This is the default behaviour.autoselects betweenmidandhighpower states based on the whether the system is on battery power or not.lowforces the gpu to be in thelowpower state all the time. Note thatlowcan cause display problems on some laptops, which is whyautoonly useslowwhen monitors are off. Selected on other profiles when the monitors are in the DPMS-off state.midforces the gpu to be in themidpower state all the time.highforces the gpu to be in thehighpower state all the time.
As an example, we will activate the low profile (replace low with any of the aforementioned profiles as necessary):
Persistent configuration
The methods described above are not persistent. To make them persistent, you may create a udev rule (example for #Profile-based frequency switching):
As another example, dynamic power management can be permanently forced to a certain performance level:
dri/ prefix.Graphical tools
- Radeon-tray — A small program to control the power profiles of your Radeon card via systray icon. It is written in PyQt4 and is suitable for non-Gnome users.
- https://github.com/StuntsPT/Radeon-tray radeon-trayAUR
Other notes
To view the speed that the GPU is running at, perform the following command and you will get something like this output:
It depends on which GPU line yours is, however. Along with the radeon driver versions, kernel versions, etc. So it may not have much/any voltage regulation at all.
Thermal sensors are implemented via external i2c chips or via the internal thermal sensor (rv6xx-evergreen only). To get the temperature on asics that use i2c chips, you need to load the appropriate hwmon driver for the sensor used on your board (lm63, lm64, etc.). The drm will attempt to load the appropriate hwmon driver. On boards that use the internal thermal sensor, the drm will set up the hwmon interface automatically. When the appropriate driver is loaded, the temperatures can be accessed via lm_sensors tools or via sysfs in /sys/class/hwmon.
Fan Speed
While the power saving features above should handle fan speeds quite well, some cards may still be too noisy in their idle state. In this case, and when your card supports it, you can change the fan speed manually.
Warning:- Keep in mind that the following method sets the fan speed to a fixed value, hence it will not adjust with the stress of the GPU, which can lead to overheating under heavy load.
- Check GPU temperature when applying lower than standard values.
To control the GPU fan, see Fan speed control#AMDGPU sysfs fan control (amdgpu and radeon share the same controls for this).
For persistence, see the example in #Persistent configuration.
If a fixed value is not desired, there are possibilities to define a custom fan curve manually by, for example, writing a script in which fan speeds are set depending on the current temperature (current value in /sys/class/drm/card0/device/hwmon/hwmon0/temp1_input).
A GUI solution is available by installing radeon-profile-gitAUR.
TV out
First, check that you have an S-video output: xrandr should give you something like
Now we should tell Xorg that it is actually connected (it is, right?)
Setting TV standard to use:
Adding a mode for it (currently supports only 800x600):
Clone mode:
Now let us try to see what we have:
At this point you should see a 800x600 version of your desktop on your TV.
To disable the output, do
Force TV-out in KMS
The kernel can recognize video= parameter in following form (see KMS for more details):
For example:
Parameters with whitespaces must be quoted:
Current mkinitcpio implementation also requires # in front. For example:
- GRUB Legacy can pass such command line as is.
- LILO needs backslashes for doublequotes (append
# 'video=9-pin DIN-1:1024x768-24@60e')
You can get list of your video outputs with following command:
HDMI audio
HDMI audio is supported in the xf86-video-ati video driver. To disable HDMI audio add radeon.audio=0 to your kernel parameters.
If there is no video after boot up, the driver option has to be disabled.
Note:- If HDMI audio does not work after installing the driver, test your setup with the procedure at Advanced Linux Sound Architecture/Troubleshooting#HDMI Output does not work.
- If the sound is distorted in PulseAudio try setting
tsched=0as described in PulseAudio/Troubleshooting#Glitches, skips or crackling and make surertkitdaemon is running. - Your sound card might use the same module, since HDA compliant hardware is pretty common. Advanced Linux Sound Architecture#Set the default sound card using one of the suggested methods, which include using the
defaultsnode in alsa configuration.
Multihead setup
Using the RandR extension
See Multihead#RandR how to setup multiple monitors by using RandR.
Independent X screens
Independent dual-headed setups can be configured the usual way. However you might want to know that the radeon driver has a 'ZaphodHeads' option which allows you to bind a specific device section to an output of your choice:
This can be a life-saver, when using videocards that have more than two outputs. For instance one HDMI out, one DVI, one VGA, will only select and use HDMI+DVI outputs for the dual-head setup, unless you explicitly specify 'ZaphodHeads' 'VGA-0'.
Turn vsync off
The radeon driver will probably enable vsync by default, which is perfectly fine except for benchmarking. To turn it off try the vblank_mode=0environment variable or create ~/.drirc (edit it if it already exists) and add the following:
If vsync is still enabled, you can disable it by editing /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-radeon.conf. See #Driver options.
Troubleshooting
Performance and/or artifacts issues when using EXA
If having 2D performance issues, like slow scrolling in a terminal or webbrowser, adding Option 'MigrationHeuristic' 'greedy' as device option may solve the issue.
In addition disabling EXAPixmaps may solve artifacts issues, although this is generally not recommended and may cause other issues.
Adding undetected/unsupported resolutions
See Xrandr#Adding undetected resolutions.
TV showing a black border around the screen
When connecting a TV using the HDMI port, the TV may show a blurry picture with a 2-3cm border around it. This protects against overscanning (see Wikipedia:Overscan), but can be turned off using xrandr:
Black screen and no console, but X works in KMS
This is a solution to the no-console problem that might come up, when using two or more ATI cards on the same PC. Fujitsu Siemens Amilo PA 3553 laptop for example has this problem. This is due to fbcon console driver mapping itself to the wrong framebuffer device that exists on the wrong card. This can be fixed by adding this to the kernel boot line:
This will tell the fbcon to map itself to the /dev/fb1 framebuffer dev and not the /dev/fb0, that in our case exists on the wrong graphics card. If that does not fix your problem, try booting with
instead.
ATI X1600 (RV530 series) 3D application show black windows
There are three possible solutions:
- Try adding
pci=nomsito your boot loader Kernel parameters. - If this does not work, you can try adding
noapicinstead ofpci=nomsi. - If none of the above work, then you can try running
vblank_mode=0 glxgearsorvblank_mode=1 glxgearsto see which one works for you, then install driconfAUR and set that option in~/.drirc.
Cursor corruption after coming out of sleep
If the cursor becomes corrupted like it's repeating itself vertically after the monitor(s) comes out of sleep, set 'SWCursor' 'True' in the 'Device' section of the /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-radeon.conf configuration file.
DisplayPort stays black on multimonitor mode
Try booting with the kernel parameterradeon.audio=0.
R9-390 Poor Performance and/or Instability
Firmware issues with R9-390 series cards include poor performance and crashes (frequently caused by gaming or using Google Maps) possibly related DPM. Comment 115 of this bug report includes instructions for a fix.
QHD / UHD / 4k support over HDMI for older Radeon cards
Older cards have their pixel clock limited to 165MHz for HDMI. Hence, they do not support QHD or 4k only via dual-link DVI but not over HDMI.
One possibility to work around this is to use custom modes with lower refresh rate, e.g. 30Hz.
Another one is a kernel patch removing the pixel clock limit, but this may damage the card!
Official kernel bug ticket with patch for 4.8: https://bugzilla.kernel.org/show_bug.cgi?id=172421
The patch introduces a new kernel parameter radeon.hdmimhz which alters the pixel clock limit.
Be sure to use a high speed HDMI cable for this.
See also
Benchmark showing the open source driver is on par performance-wise with the proprietary driver for many cards.